Air-cooled vs. Water-cooled Chillers
General Introduction
Heating issues are a common problem in many industries. Industrial processes, such as the manufacturing of products, often lead to reduced efficiency, equipment damage, and product quality issues. Fortunately, chillers provide an effective solution for eliminating heat and controlling temperatures in a wide range of industrial applications. Chillers can provide accurate temperature control by regulating the flow of chilled water to the process or product being cooled. This makes it possible to precisely manage the temperature, ensuring that the manufacturing process goes without a hitch and that the final products satisfy the necessary standards for quality and safety.
In addition to eliminating heat and controlling temperatures, chillers are also useful for reducing energy costs in industrial processes. By using a chiller to cool industrial processes, companies can reduce their energy consumption and costs as compared to traditional air conditioning systems. In this blog, we will be learning about air-cooled and water-cooled chillers and how they are different from each other. Let us take a deep dive into the subject and learn more about two different types of coolers used in industry for temperature control.
Air-cooled chillers
An air-cooled chiller is a type of refrigeration system that utilizes air as the cooling medium. These air-cooled chillers are extensively taken into account in commercial and industrial settings for cooling large spaces, such as offices, factories, and warehouses. They are an efficient and cost-effective solution for cooling large buildings because they require less maintenance and are easier to install than water-cooled chillers.
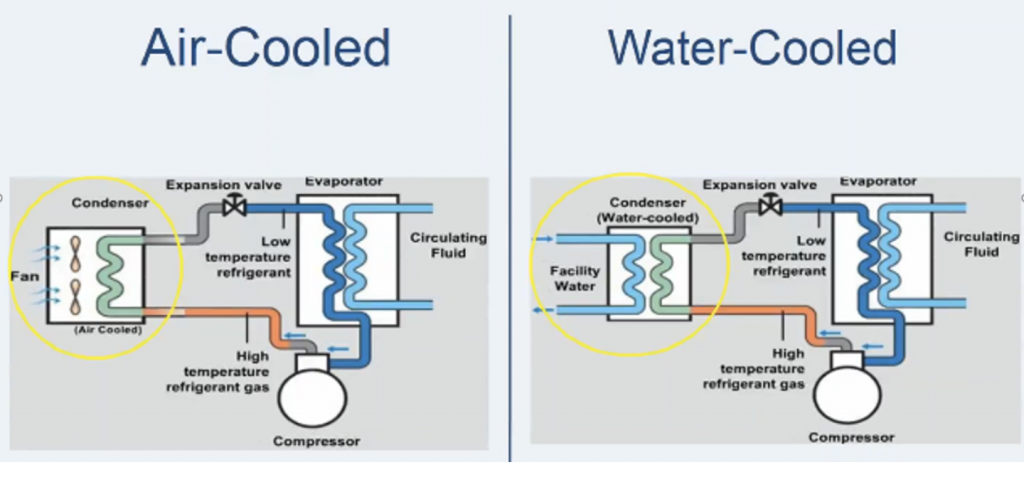
Air-cooled chillers function by using a refrigerant, such as R-410a, to absorb heat from the air inside the building. The refrigerant then passes through a compressor, which increases its temperature and pressure. The hot refrigerant is then passed through a condenser, where it releases its heat into the outside air. The refrigerant comes back to the evaporator, where it absorbs more heat. This whole cycle repeats again and again. This is how an air-cooled chiller in an industry functions.
Some benefits of air-cooled chillers include:
- Easy installation and maintenance: air-cooled chillers do not require a cooling tower or water supply, making them easier to install and maintain.
- Energy efficiency: air-cooled chillers use less water and energy compared to watercooled systems, making them more environmentally friendly.
- Flexibility: Air-cooled chillers can be used in a variety of settings and applications, making them a versatile cooling solution.
- Cost-effectiveness: air-cooled chillers are generally less expensive to install and operate compared to water-cooled systems, making them a cost-effective cooling solution.
Water-cooled Chillers
Water-cooled chillers are a type of refrigeration system that uses water as a cooling medium to remove heat from a process or space being cooled. These chillers use a cooling tower or an open or closed-loop water system to reject the heat absorbed from the process.
Water-cooled chillers provide an efficient and cost-effective cooling solution for industries that require a constant supply of cool water. They are commonly used in large commercial buildings, data centres, and industrial processes such as plastics manufacturing, chemical production, and pharmaceuticals.
Some benefits of water-cooled chillers include:
- Energy efficiency: Water-cooled chillers can operate more efficiently than air-cooled chillers, which can result in lower energy costs.
- Reduced noise: Water-cooled chillers tend to produce less noise than air-cooled chillers, making them a better option for noise-sensitive applications.
- Higher capacity: Water-cooled chillers are capable of providing a higher cooling capacity than air-cooled chillers, making them suitable for larger applications.
- Longer lifespan: Water-cooled chillers typically have a longer lifespan than air-cooled chillers, which can provide a better return on investment in the long run.
Air-cooled chillers vs. water-cooled chillers: The Major Differences
Air-cooled chillers and water-cooled chillers are two types of chillers used in industries to provide cooling for various applications. The major differences between them are:
- Cooling Method: The primary difference between air-cooled chillers and watercooled chillers is the method used to remove heat from the chiller. Air-cooled chillers use air as the cooling medium, while water-cooled chillers use water.
- Efficiency: Water-cooled chillers are generally more efficient than air-cooled chillers. Water is a better conductor of heat than air, which means that water-cooled chillers can remove heat more effectively. This means that water-cooled chillers can provide the same level of cooling with less energy consumption than air-cooled chillers.
- Maintenance: Air-cooled chillers are generally easier to maintain than water-cooled chillers. Air-cooled chillers have fewer components and require less maintenance than water-cooled chillers. Water-cooled chillers require regular maintenance of the water treatment system to prevent corrosion, scale buildup, and biological growth.
- Noise Level: Air-cooled chillers are generally louder than water-cooled chillers. This is because air-cooled chillers use fans to circulate air, which can be noisy. Watercooled chillers use water pumps, which are much quieter.
- Installation: Water-cooled chillers require additional infrastructure for water supply and drainage, while air-cooled chillers do not. This makes air-cooled chillers easier and less expensive to install.
- Environmental Impact: Water-cooled chillers use water as a cooling medium, which can have an impact on the environment. Water usage and discharge must be carefully managed to avoid negative environmental impacts. Air-cooled chillers do not use water, so they have a lower environmental impact.
Ultimately, the choice between air-cooled and water-cooled chillers depends on various factors, such as the cooling requirements, installation constraints, and maintenance capabilities.
The Final Verdict: Air-cooled Chillers vs. Water-cooled Chillers
To conclude, both air-cooled and water-cooled chillers have their advantages and disadvantages, and choosing between them depends on several factors, such as cooling requirements, space availability, and budget. Air-cooled chillers are generally more compact, easier to install, and suitable for smaller applications, while water-cooled chillers offer greater energy efficiency and precise temperature control, making them suitable for larger industrial processes. Ultimately, selecting the right chiller for a particular application is crucial for ensuring optimal cooling efficiency, reducing energy costs, and maintaining product quality and safety.






